Here is a list of some common error messages along with some cures to the trouble. |
|
They
are our those pesky problems your computer has during
normal operation. Do not worry, they are normal,
occasionally these happen. This page I hope will give you
some tips on how to deal with these pesky messages and
hopefully end them.Insert disk with COMMAND.COM in drive A and press and key to continueThis means that you computer cant find the dos or the windows files. Stick a system disk in the drive (A) and press enter. If you have a disk in the drive already, you may need to make it a system disk or boot from the hard drive. To make a system disk you have a couple of options. One is to use the control panel in Windows 9x. Double clicking the Add/Remove icon brings up a window which will help make that disk you need. Below is an illistration of that window: |
|
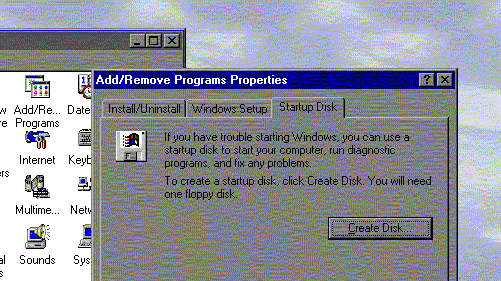 |
| From a DOS prompt or window it is a little more complicated. Lets start with windows 9x again. You have to be sure you are in the C:\windows\command directory. To get there you would just type in cd (for change directory) then C:\windows\command and press enter. Then type in "sys C:\windows A"and press enter. the illistration below shows the commands in sequence. | |
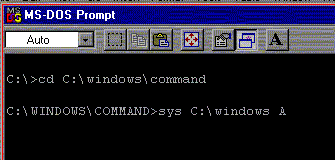 |
|
| In real DOS mode the typing would still remain the same. If you have DOS, windows 3.x, or a version other than Windows 9x, you should be able to get the "sys" string mentioned above in the directory "DOS". then you would type in "cd C:\DOS" instead. That should get you going. Below is a list of stitches for the sys command. | |
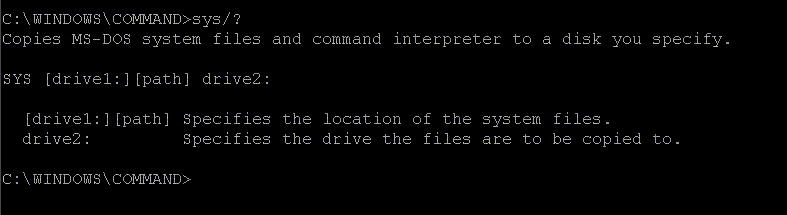 |
|
| Invalid media of Track 0 bad disk unusable Format terminated | |
| When attempting to format
a disk with the previous method or another, this message
means that the location for the system files needed for
system disk are damaged. The disk is probably no good. If
this error occurs during the format of a hard drive, it
means deep
trouble. The drive is no good for a bootable drive- you
may be able to transfer information from this drive to
another but you will need to boot from another location. This also happens when trying to boot some bad disks. The error then displays "Disk Unusable." |
|
| Access denied | |
| This message is
given after trying to write or delete on a
write-protected disk. On a normal floppy the disks are
write protected by the sliding clip on the top rear
corner of the disk. 5 1/4 floppies have tape. If this is
happening on files located on the hard disk, that file ir
protected. To disable protection on a file in windows, you must run an attribute on the file. This also is done in DOS mode. You must get to the directory where the file is located and type in "attrib filename" to change the protection. The following picture shows the options for "attrib". |
|
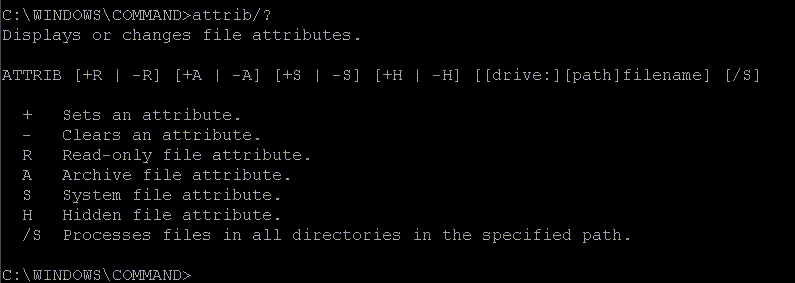 |
|
| Notice that typing the /? stitch was used to get a list of the commands. Most any DOS exe file will react to this stitch. The read only attribute is the protect that you are probably looking for when saving or editing a file. | |
| Divide Overflow | |
| This one leaves you no options. It means that the computer has tried to do an operation that is not possible; divide a number by zero. The only thing you can do from this point is to restart. If the computer was booting, you will need to reboot. If it was just a program that was running, you usually would have recieved the "Illegal operation" error in the message box. You will have to exit and restart the operation. | |
| Drive not ready Abort, Retry, Fail? This message is returned after the computer attempts to access a drive that had no media or disk in it. Make sure the drive is closed, the disk is formatted correctly, or that the drive is setup properly. You just press the letter corresponding the next action to continue. R for retry, F for fail, or A for abort. |
|
| Insufficient Memory | |
| This message
means that the computer has temporarily run out of memory
or does not have enough memory to complete the operation.
You may want to check to see that the memory is set up
right or that a memory manager is running. The "mem"
command displays the status of the memory usage. Also
displayed is the maximum allowable size of program to
run. If you are getting this message in Windows 95, you may want to check the autoexec.bat and config.sys files to see how the emm386.exe file is set to run. It should be allowed to run on its own settings. If you have to run it, set it to auto mode. There is more information in the Windows directory called config.txt and msdosdrv.txt. These files are opened with the notepad and are very useful. DOS does not start the same memory manager. It uses the himem.sys to test and use the high memory addresses. You may also turn on the emm386 by specifying it in your config.sys file. MS DOS has a list of text and help files in the DOS directory that will be good resources as well. |
|
| Bad command or file name | |
| You must have
typed in something that the computer did not understand
or a filename the computer could not find. Make sure the
file is in the same directory that you are in or that you
spelled it correctly. If you see this at startup then something in the autoexec.bat or config.sys is mispelled or looking in the wrong directory. These files can be edited using the editor in the DOS or windows\command directories. Just run the edit program or enter "type filename" to see the file displayed. These can be edited in Win95 by right clicking on them and selecting edit. |
|
| Bad or Missing filename | |
| Once again your computer cannot find a file. This could happen during startup or DOS prompt. See Bad command or Filename. | |
| General Failure | |
| Dos can often have a problem with different floppies, hard drives, of file formats and spit out an error. But, when it gets really confused, you see this error. You may want to check the format of the media, see that it isconfigured correctly, find out if it is inserted correctly: all of these things could have that effect. Even check that you have inserted the right type of media into the drive. | |
| Incorrect DOS Version | |
| This message is
displayed by DOS when a program from a different version
of DOS is run from your computer. The different versions
of DOS are not compatible in some programs. The programs
in DOS were upgraded and changed over time to make them
better or improve functionality over time. These changes
generate the problem. If you copied some of the DOS files from a friends computer and put them on your computer you may get this error message when you run the program. You may also get this error from running a buddies startup disk. If you've booted from a disk and get this message when you start working with the files on your hard drive, you may have to check the version of the disk you booted from. To check your DOS version, type "ver" at the DOS prompt. |
|
| Insufficient disk space | |
| Apparently, the
disk you intended to store information on is now too full
to store more information. This can happen with most any
storage media. To check to make sure in DOS, you could
run check disk, a utility checking hard drive status.
Just type in "chkdsk" from
the DOS directory (if running DOS or win3.x). If yours is
an IBM the Dosshell will display free space information. In windows 3.x or 9x you can use the file manager. The free space is displayde if you click on the drive you wish to check from within the directory tree. Notice the illistrations below. The file manager is shown at the left, windows explorer from win9x is shown on the left. In both examples, the space information is on the bottom left. |
|
 |
|
| You will notice that they are pretty much the same thing. You can also use the DriveSpace3 program from the system tools on the Accessories folder on the start menu. That program shows a nice graphical chart. Another way is to right click and select poperties from within the above programs. | |
| Internal stack failure, system halted | |
| Reboot your
computer. You may need a system disk like the one you
created at the installation of windows or as described
above in "Insert disk with COMMAND.COM." Next, add the following line to your hard disks config.sys file (also described above somewhere): Stacks 9,256 When you reboot your computer with the new config.sys, it should be back to normal. If not, the number 9 after the "stacks" can be changed to 12. If still wrong try 15 (notice the changes in multiples of three.) Just do not change the 256 as it needs to be the same. |
|
| Sector not found | |
| DOS is having trouble finding information on your disk. Try running a scan disk or a check disk on the media. If you have not backed up the information on the disk, do so as soon as possible because chances are that the disk is about to die or in need of formatting. | |
| Here is a little table of common IRQ assignments | |
| Some times after an upgrade, you can't get your computer to boot. It could be the conflict of two devices trying to share IRQ assignments. This list is a reference to some common assignments. You may be better off to check your assignments in your Bios or in windows and draw out your own table and see which IRQ's are available on your system. |
| IRQ # Commonly ascociated | Device commonly assigned |
| IRQ 0 | Timer interrupt |
| IRQ 1 | Keyboard interrupt |
| IRQ 2 | Cascade to IRQ 9 |
| IRQ 3 | COM 2 and COM 4 |
| IRQ 4 | COM 1 and COM 3 |
| IRQ 5 | LPT 2 (parallel printer port) |
| IRQ6 | Floppy Disk |
| IRQ 7 | LPT 1 (parallel printer port) |
| IRQ 8 | Real Time Clock |
| IRQ 9 | Cascade to IRQ 2 |
| IRQ 10 | Available to user |
| IRQ 11 | Available to user |
| IRQ 12 | Mouse Port on PS/2 |
| IRQ 13 | 80X87 Math Coprocessor |
| IRQ 14 | Hard Disk |
| IRQ 15 | Available to user |
| Meet the Maker! | Find a Book! | |